Eczema (also known as atopic dermatitis) is most common in infants where it occurs in around 1 in 5 children under 2 years of age.
It can also occur in older children and adults but usually improves with age. Although eczema can be effectively treated and managed, no cures are currently available.
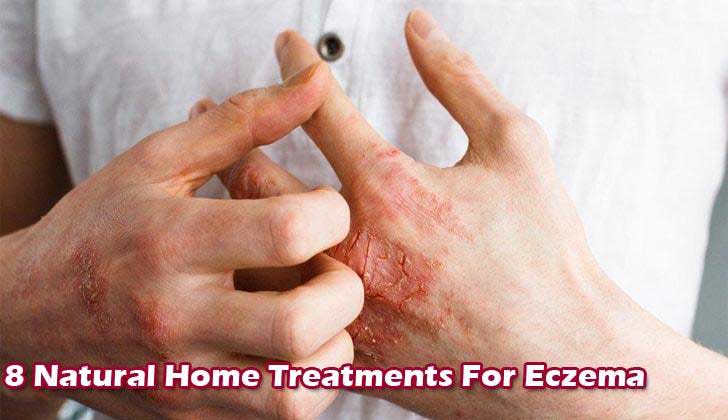
Eczema is a condition where patches of skin become inflamed, itchy, red, cracked, and rough. Blisters can also occur. It affects a large section of the American population to a lesser or greater degree.
The word eczema is also used specifically to refer to atopic dermatitis, the most common type of eczema.
What is Eczema?
The term eczema is used in two different ways. It can be used widely to describe any rash-like skin conditions. Or it can be used to describe atopic dermatitis, a chronic skin condition that commonly starts during infancy and continues through into childhood.
Some people outgrow the condition while some people will continue to have it into adulthood. The word “atopic” refers to a collection of diseases involving the immune system, including atopic dermatitis, asthma, and hay fever. “dermatitis” means inflammation of the skin.
Infants
- Rashes commonly appear on the scalp and cheeks.
- Rashes usually bubble up before weeping fluid.
- Rashes can cause extreme itchiness, which may lead to trouble sleeping. Continuous rubbing and scratching can lead to skin infections.
Adults
- Rashes commonly appear in creases of elbows or knees or nape of the neck.
- Rashes cover much of the body.
- Rashes can be especially prominent on neck, face, and around the eyes.
- Rashes can cause very dry skin
- Rashes can be permanently itchy.
- Rashes can cause scaly skin (more scaly than in children).
- Rashes can lead to skin infections.
Adults who developed atopic dermatitis as a child but no longer experience the condition may still have dry or easily irritated skin, hand eczema, and eye problems.
The appearance of skin affected by atopic dermatitis will depend on how much a person scratches and whether the skin is infected. Scratching and rubbing irritate the skin further, increases inflammation, and makes the itchiness worse.
Types of Eczema
There are many different types of eczema. Other variants include:
- Allergic contact eczema (dermatitis) – a skin reaction following contact with a substance that the immune system recognizes as foreign.
- Contact eczema – a localized reaction where the skin has come into contact with an allergen.
- Dyshidrotic eczema – irritation of the skin on palms of hands and soles of feet characterized by blisters.
- Neurodermatitis – scaly patches of skin on head, forearms, wrists, and lower legs caused by a localized itch such as an insect bite.
- Nummular eczema – circular patches of irritated skin that can be crusted, scaling, and itchy.
- Seborrheic eczema – oily, scaly yellowish patches of skin, usually on scalp and face.
- Stasis dermatitis – skin irritation on lower legs, usually related to circulatory problems.
Top 10 Symptoms Of Eczema
Topical corticosteroid creams and ointments – these are a type of anti-inflammatory medication and should relieve the main symptoms of eczema, such as skin inflammation and itchiness.
If ineffective, systemic corticosteroids can be prescribed. These are either injected or taken by mouth; they are only used for short periods.
Antibiotics if there is an overlying bacterial skin infection.
Medications to treat fungal and viral infections.
Antihistamines that cause drowsiness are often recommended as these can help to reduce the risk of night-time scratching.
Topical calcineurin inhibitors – a type of drug that suppresses the activities of the immune system; it decreases inflammation and helps prevent flare-ups.
Barrier repair moisturizers – these reduce water loss and work to repair the skin.
Phototherapy can be prescribed to treat mild to moderate dermatitis. It involves exposure to ultraviolet A or B waves, alone or combined.
The skin will be monitored carefully. Even though the condition itself is not presently curable, there should be a particular treatment plan to suit each case.
Even after an area of skin has healed, it is important to keep looking after it, as it may easily become irritated again.

8 Natural Home Treatments For Eczema
1) Fight The OutBreaks With Food
Fight the outbreaks with food Many health conditions, both skin-related or not, can be helped by following the correct dietary regiment and Eczema makes no exception.
The best way to go is to eat as much raw and organic food as possible. This type of meal is natural to the human body and nourishes it best. On the other hand, some foods can irritate the skin and worsen the problem.
Avoid processed foods, as they are full of chemicals, artificial sweeteners, and saturated fats. Also, try staying away from alcohol, caffeine, meat, gluten, and dairy.
2) The Magic Powers Of Coconut Oil
The magic powers of coconut oil cold-pressed, organic coconut oil has become a sensation and rightfully so. Even large and well-respected fashion magazines are now advertising the natural healing powers of coconut oil.
It is great for the skin and just perfect for treating Eczema. Coconut oil contains a very rare substance called lauric acid, it helps fight bacteria and microorganisms that can cause skin conditions such as eczema.
What you can do is substitute all the oils you use in the kitchen with coconut oil and also use it as a moisturizer. It soothes the skin and penetrates deeply to protect it from unwanted environmental and chemical damage.
3) C For Care Vitamin
C for Care Vitamin C is a great way to protect and nourish your skin and can help fight eczema outbreaks. The wonderful substance contains essential nutrients that strengthen the immune system and help it fight infection.
That is why vitamin C is also very effective in treating the common cold. It also has anti-inflammatory effects and protects the cells from stress.
You can either purchase vitamin C supplements, or you can try eating more fresh fruits and vegetables, especially orange and yellow ones.
4) Say No To Stress
Say no to stress Often the reason for skin conditions stems from increased stress levels. Stress is functional, it makes you strive to achieve certain goals, it keeps you alert and is a natural bodily mechanism, so long as it is not excessive.
Too much stress is damaging for all organs, not to mention the severe psychological damages it can cause.
Sometimes a disease, such as eczema, can be psychosomatic, meaning that there are no physiological factors that explain its onset and development.
Rather, it has stemmed from psychological issues that have manifested as physical symptoms. eczema may be your body’s way of telling you that you are enduring too much stress and pressure.
5) Salt Baths For Clear Skin
Salt baths for clear skin Bath salts come in many varieties and scents and as long as they do not have any chemical additives, they are a wonderful way to keep eczema away.
Dermatological studies have shown that bath salts smooth out the skin, reduce redness and inflammation, and relieve itchiness. All you have to do is dilute a few tablespoons in your bathtub and take a relaxing soak.
6) Aloe Vera
Moisturize with aloe vera and Vitamin e aloe vera is one of the miracle workers of nature. It is no wonder that so many cosmetics companies use it in their products – it is one of the most potent moisturizers and skin-soothers.
Vitamin E, on the other hand, is used in many beautifying recipes due to its anti-inflammatory properties. You can combine equal parts of the two and pad the skin gently with a cotton ball.
7) Soak in Oatmeal
Soak in oatmeal Taking an oatmeal bath is one of the most popular eczema treatments. Blend about a cup of oatmeal into a very fine powder, place it in your bathtub, and pour hot water on top.
Then take a 15-minute soak. Oatmeal is so popular because it soothes itchy and irritated skin, it also helps with redness.
8) Essential Oil Remedy
Essential oil remedy essential oils are always a great way to improve your skin condition. They rejuvenate and moisturize the cells, along with helping them fight infection and skin roughness.
For best result, mix just a drop of chamomile or yarrow in jojoba or almond oil, then rub all over the skin.
Eczema may be a tough problem to deal with, but as long as you take the steps listed above a part of your routine, you will feel the difference.
Foods That Can Help Eczema
- Apples.
- Celery.
- Cucumber.
- Spinach.
- Cranberry.
- Avocado.
- Asparagus.
- Blueberry.
- Watermelon.
- Elderberry.
